What Is Extraterritorial Jurisdiction?
Extraterritorial Jurisdiction (ETJ) in Texas refers to the area outside a city's boundaries where the city has limited regulatory authority. Established by the Texas Local Government Code (Chapters 42, 43, and 212) in 1963, ETJs serve as buffer zones for future growth beyond current city limits.
However, ETJs can be a source of contention for landowners and developers as they present unique challenges for how their land is used. We'll cover a few key considerations in this short guide on Texas ETJs, but because the extent of these powers can vary between municipalities, you'll want to consult local government officials or legal experts to make informed decisions.
Determining if Your Property is in an ETJ Zone
Here's how to find out if your property lies within an ETJ or is an area that may become an ETJ:
Consult City Maps
Cities are required by Texas state law to maintain updated maps showing their boundaries and ETJs as they grow. These maps are available at city offices or on official websites.
Note: Even if a city expands, it cannot extend its ETJ zone into another city's ETJ zone. These zones also cannot be reduced without written consent from the city council.
Visualize ETJ Zones With Acres
If you're a land professional working in Texas, having easy access to a statewide ETJ map can save you a lot of time. Acres.com provides tools for visualizing data like ETJ zones, wells, and more so you can keep this data at your fingertips for land research and valuation.
Paired with the largest land sales database available and more tools for land research, prospecting, and marketing, Acres is a true one-stop-shop for land data and mapping. To learn more and get access, book a demo with our team!
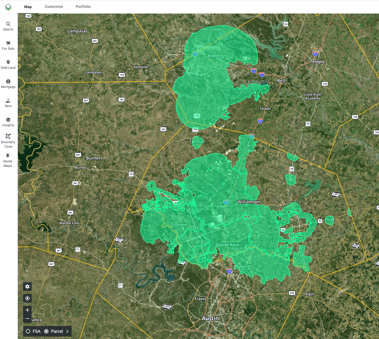
What to Expect in ETJ Zones
While cities can enforce certain regulations in an ETJ, their authority is not unlimited. Depending on the municipality, they may regulate subdivisions, infrastructure, some building standards, and land use.
Despite being subject to some city regulations, properties in an ETJ may not receive city services like water, sewer, or emergency services. These properties are also candidates for future annexation, which can change taxation and access to city services.
How ETJ Zones Affect Landowners
Landowners within an ETJ are subject to certain city regulations but cannot participate in city elections, limiting their influence over decisions that impact their property.
For example, cities may impose rules on obtaining building permits, land use, construction standards, and development within the ETJ. These regulations can affect construction plans and business activities.
What Can Landowners Do?
Get started by familiarizing yourself with specific regulations that apply within your ETJ.
From there, you'll want to keep up-to-date. Attending city council meetings and public hearings is a great way to voice concerns and stay informed about city plans, annexations, and changes to ETJ boundaries.
You can also join advocacy groups, like the Texas City Limits Coalition, that advocate for landowners' rights in ETJ zones.
What to Consider When Buying Land in an ETJ Zone
Buying land in a Texas ETJ zone means navigating specific city rules that shape how you can use the property. When considering a property, thoroughly research the ETJ’s regulations to ensure your plans align with city requirements. Understand how these rules might impact your intended use and future property value. A few questions you may want to ask:
- What are the current zoning regulations for this ETJ area?
- Are there any restrictions on building or land use?
- Is future annexation likely, and how could it impact the property?
- What city services are available, and which are not provided?
- Are there any planned developments that might affect the ETJ?
- How do ETJ rules influence property value and taxes?
Working with an experienced land professional can help you navigate ETJs and is an important step in due diligence.
FAQs
Why Were ETJ Zones Created?
ETJ zones were established to promote orderly growth and to plan for the future expansion of cities. When first established, the Texas Legislature originally stated ETJs are designed "to promote and protect the general health, safety, and welfare of persons residing in and adjacent to" cities.
How Large Can an ETJ Zone Be?
In Texas, the size of an ETJ depends on the city's population:
- Fewer than 5,000 residents: Up to 0.5 miles
- 5,000 to 24,999 residents: Up to 1 mile
- 25,000 to 49,999 residents: Up to 2 miles
- 50,000 to 99,999 residents: Up to 3.5 miles
- 100,000 or more residents: Up to 5 miles
Can an ETJ Exceed These Limits?
A city's ETJ may differ based on local agreements or specific circumstances. A city cannot expand its ETJ into another city's ETJ without consent. Reduction of an ETJ also requires written consent from the city council.
Final Thoughts
Extraterritorial Jurisdiction zones in Texas have significant implications for landowners and developers. While they allow cities to plan for future growth, they also impose regulations on properties outside city limits. If you own or are thinking of buying a property in or near an ETJ zone, understanding how these regulations will impact land use and future plans is an important part of due diligence.
