As biodiesel demand rises, so do opportunities to develop infrastructure, grow feedstock, and invest in energy-driven land. The Biodiesel Plants map from Acres.com gives you a national view of active sites—so you can evaluate nearby land for strategic acquisitions, development potential, and supply chain alignment.
What are Biodiesel Plants?
Biodiesel plants—also known as biodiesel production facilities or biorefineries—convert raw materials like vegetable oil, animal fats, and recycled grease into biodiesel, a renewable diesel alternative.
These facilities play a vital role in the clean energy economy by transforming organic feedstocks into low-emission, biodegradable fuels that help reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Map of U.S. Biodiesel Plants
Accessible in Acres’ Layer Library, the Biodiesel Plants map visualizes active biodiesel manufacturing facilities across the U.S. and offers key insights, including:
- Facility names and company ownership
- Geographic distribution by state
- Site-level data for deeper analysis
To explore this map and hundreds of other layers, connect with our sales team today!
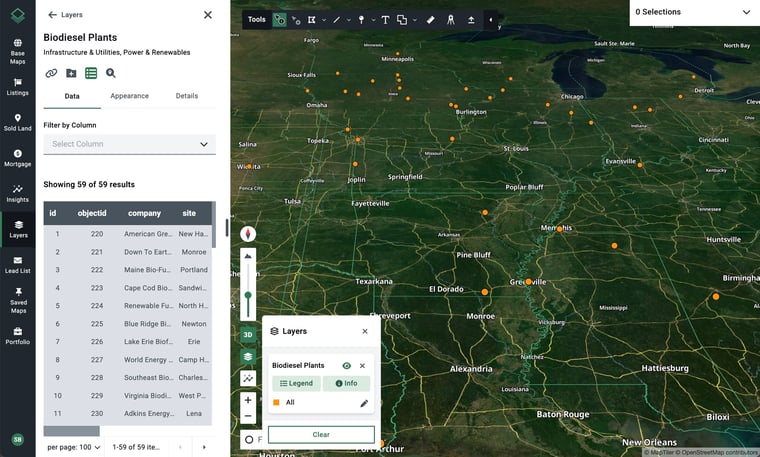
Acres’ nationwide biodiesel plant data is derived from the Energy Information Administration (EIA).
Environmental Impact
Potential Benefits
- Lower Emissions: Using 100% biodiesel (B100) can cut greenhouse gas emissions by up to 75% compared to traditional petroleum diesel.
- Renewable and Biodegradable: Derived from natural sources, biodiesel breaks down faster than fossil fuels.
- Energy Independence: Boosts U.S. energy security by reducing dependence on imported oil.
- Rural Economic Growth: Supports job creation in farming, logistics, and production relating to biodiesel supply chains.
Potential Risks
- Land Use Change: Converting forests or grasslands into cropland for biodiesel feedstocks can lead to deforestation, biodiversity loss, and increased emissions.
- Production Costs: Feedstock price volatility and processing complexity can make biodiesel more expensive.
- Water Consumption: Cultivation of feedstocks like soy or hay can be water-intensive.
Pro Tip: Use Acres' Layer Library to evaluate local water resources and zoning when exploring areas for biodiesel production.
Considerations for Landowners and Investors
- Zoning and Permitting: Ensure zoning compatibility for industrial or agricultural use.
- Infrastructure Access: Proximity to roads, railways, or ports increases viability.
- Water Availability: Access to reliable water sources is essential for feedstock growth.
- Environmental Impact: Understand the trade-offs of converting natural land to biodiesel production land.
- Economic Opportunity: Biodiesel plants can stimulate local economies and boost land value.
Final Thoughts
As the clean energy transition accelerates, understanding where and how biodiesel is produced matters more than ever. With Acres’ Biodiesel Plants map, you can explore the intersection of renewable energy and land use—and make data-backed decisions.
