When evaluating land, factors like soil quality, zoning laws, and access to infrastructure are often top of mind. But have you considered how nearby power plants affect land values?
Whether it's increased energy accessibility, potential restrictions, or shifting buyer interest, power plants can play a major role in land transactions. With the Acres.com power plants map, you can pinpoint these facilities and assess their impact with precision.
What is a Power Plant?
A power plant converts energy sources, such as coal, solar, nuclear, and wind, into electricity to power homes and businesses. These facilities vary in type, size, and environmental impact.
Map of U.S. Power Plants
Acres offers an interactive Power Plants Map, providing nationwide insights into plant site locations. Available in our Layer Library, this tool includes key data such as plant type, ownership, and electricity production capacity.
Connect with our sales team today to explore hundreds of data layers!
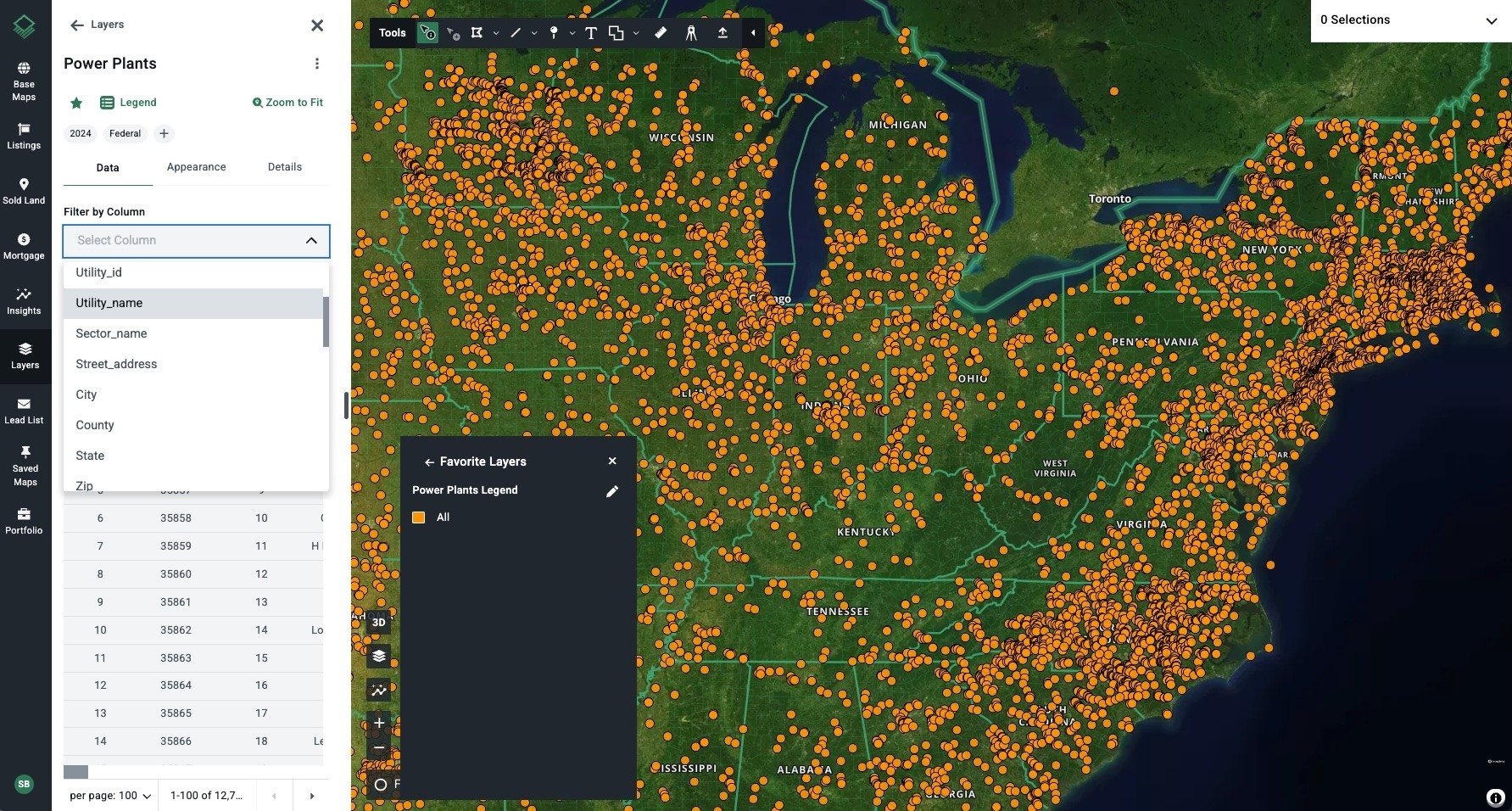
Acres’ nationwide power plant data is derived from the Energy Information Administration (EIA).
Types of Power Plants
The most common types of power plants include:
Thermal Power Plants
- Coal-Fired Plant: Burns coal to generate steam, which powers turbines.
- Natural Gas Plant: Uses gas combustion to drive turbine generators.
- Nuclear Power Plant: Generates heat from nuclear fission, producing steam to spin turbines.
Renewable Energy Plants
- Solar Plower: Converts sunlight into electricity.
- Wind Power: Uses wind turbines to generate electricity.
- Geothermal Plant: Extract heat from the earth to produce electricity.
Hydroelectric Power Plants
Utilize flowing water from rivers or dams to generate electricity.
Hybrid Power Plants
Combines multiple energy sources for greater efficiency and reliability.
Considerations for Landowners and Investors
Environmental and Health Factors
- Air Quality Concerns: Fossil fuel power plants release pollutants like coal ash (coal combustion residuals) which contain heavy metals and other harmful substances that can impact local air quality.
- Radiation Concerns: Radiation safety measures and emergency evacuation plans near nuclear plants may be of importance to know.
- Noise Pollution: Generators and turbines can create continuous noise.
- Water & Soil Contamination: Industrial runoff may affect local water and land quality.
- Wildlife Impact: Energy infrastructure could disrupt local ecosystems.
Property Value and Development
- Market Demand and Resale Value: Land near power plants may see reduced demand due to environmental concerns.
- Aesthetic Issues: Industrial structures and emissions can affect visual appeal.
- Development and Land Use Restrictions: Certain zoning laws may limit future development near power plants.
Legal and Financial Factors
- Buffer Zones: Minimum distance regulations may apply to residential properties near power plants.
- Eminent Domain Risks: Governments may acquire land for energy expansion projects.
- Higher Insurance Costs: Proximity to industrial sites can raise insurance costs due to environmental and safety risks.
- Lending Challenges: Lenders may be hesitant to approve loans for land near power plants due to potential risks.
Final Thoughts
Power plants don’t just generate electricity—they shape land values, influence investment strategies, and impact local communities. Whether you’re a landowner, investor, or broker, understanding how proximity to power plants affects land is key to making informed decisions.
From buffer zones to buyer perception, power plants matter. Explore Acres’ Layer Library to map energy infrastructure and make confident, data-backed decisions.
